C++ has some version of international standards.
- C++98
- C++03
- C++11
- C++14
- C++17
- C++20
In this article, we show how to display the C++ version in various compilers.
Other Languages
Sample Code for Displaying C++ Version
You can take the version by outputting the built-in macro __cplusplus.
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << __cplusplus << std::endl;
return 0;
}Output with gcc
Output in Default Option
$ g++ --version
g++ (Ubuntu 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) 11.4.0
Copyright (C) 2021 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.$ g++ main.cc && ./a.out
201703If you use the gcc of 11.4.0 version, 201703 is shown as the result.
It means that the version is C++17.
Output with the “std” option
In gcc, you can choice the C++ version with specifying the “std” option as follows.
$ g++ -std=c++98 main.cc && ./a.out
199711$ g++ -std=c++03 main.cc && ./a.out
199711$ g++ -std=c++11 main.cc && ./a.out
201103$ g++ -std=c++14 main.cc && ./a.out
201402$ g++ -std=c++17 main.cc && ./a.out
201703$ g++ -std=c++20 main.cc && ./a.out
202002Note that support is experimental for some newer version according to man of g++.
c++20
c++2a
The 2020 ISO C++ standard plus amendments. Support is experimental, and could change in incompatible ways in future releases. The name c++2a is deprecated.Output with clang
The default of the clang that has the version of 14.0.0 is C++14.
$ clang++ --version
Ubuntu clang version 14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1
Target: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
Thread model: posix
InstalledDir: /usr/bin$ clang++ main.cc && ./a.out
201402You can specify the version of C++ by the “std” option.
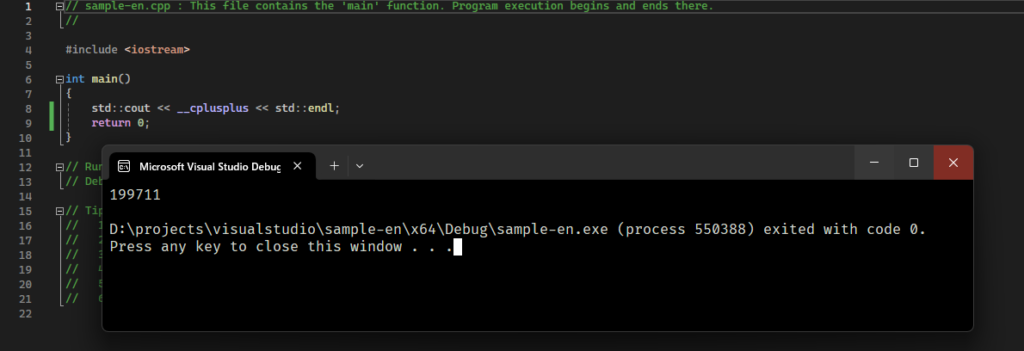
Output with Visual Studio 2022
Only the string of 199711 is shown in Visual Studio 2022.
You cannot get what you need in this way.
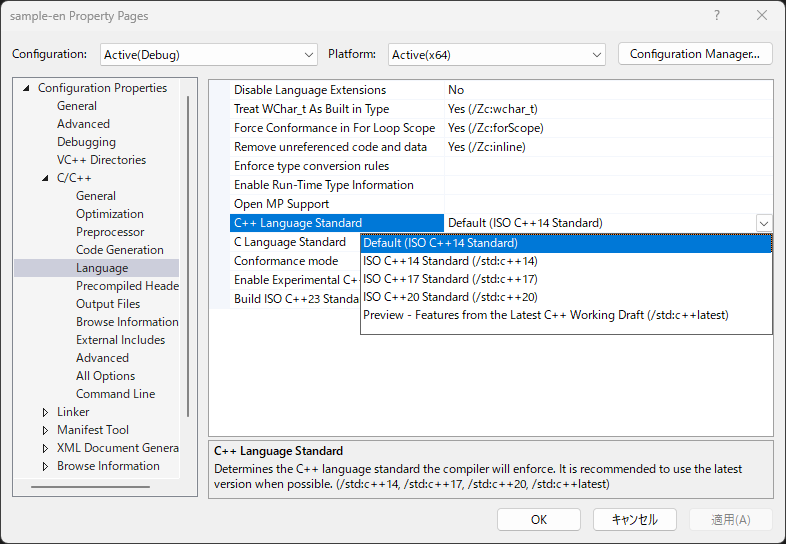
You can get the version of C++ by another way.
It is specified in the property of the project.


Comments